II B.Tech II Sem CSE Java Lab Exercise - 2 d(Operations, Expressions, Control-flow, Strings)
d) Implementing StringBuffer
Aim: To write a JAVA program using StringBuffer to delete, remove character
Description:
Program:
class stringbufferdemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
StringBuffer sb1 = new StringBuffer("Hello Gandi");
sb1.delete(0,6);
System.out.println(sb1);
StringBuffer sb2 = new StringBuffer("Some Content");
System.out.println(sb2);
sb2.delete(0, sb2.length());
System.out.println(sb2);
StringBuffer sb3 = new StringBuffer("Hello Netaji");
sb3.deleteCharAt(0);
System.out.println(sb3);
}
}
Output:
II B.Tech II Sem CSE Java Lab Exercise - 2 c(Operations, Expressions, Control-flow, Strings)
c) Merge sort:
Aim: To write a JAVA program to sort for an element in a given list of elements using merge sort
Description:
Program:
import java.util.*;
class mergedemo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int n1,n2,i,j,k;
int a[ ]=new int[20];
int b[ ]=new int[20];
int c[ ]=new int[20];
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter number of elements in first array:");
n1 = s.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter sorted elements of first array:");
for (i = 0; i < n1; i++)
a[i] = s.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter number of elements in second array:");
n2 = s.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter sorted elements of second array:");
for (j = 0; j < n2; j++)
b[j] = s.nextInt();
i = 0;
j = 0;
k = 0;
while((i < n1) && (j <n2))
{
if(a[i] > b[j])
c[k++] = b[j++];
else
c[k++] = a[i++];
}
while(i < n1)
c[k++] = a[i++];
while(j < n2)
c[k++] = b[j++];
System.out.println("After merging the elements are:\n");
for(i = 0; i < (n1 + n2); i++)
System.out.print("\t"+c[i]);
}
}
Output:
II B.Tech II Sem CSE Java Lab Exercise - 2 b(Operations, Expressions, Control-flow, Strings)
b) Bubble sort
Aim: To write a JAVA program to sort for an element in a given list of elements using bubble sort
Description:
Program:
import java.util.Scanner;
class bubbledemo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int n, i,j, temp;
int a[ ]=new int[20];
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter total number of elements:");
n = s.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter elements:");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
a[i] = s.nextInt();
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n-1;j++)
{
if(a[j]>a[j+1])
{
temp=a[j];
a[j]=a[j+1];
a[j+1]=temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println("The sorted elements are:");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
System.out.print("\t"+a[i]);
}
}
Output:
II B.Tech II Sem CSE Java Lab Exercise - 2 a(Operations, Expressions, Control-flow, Strings)
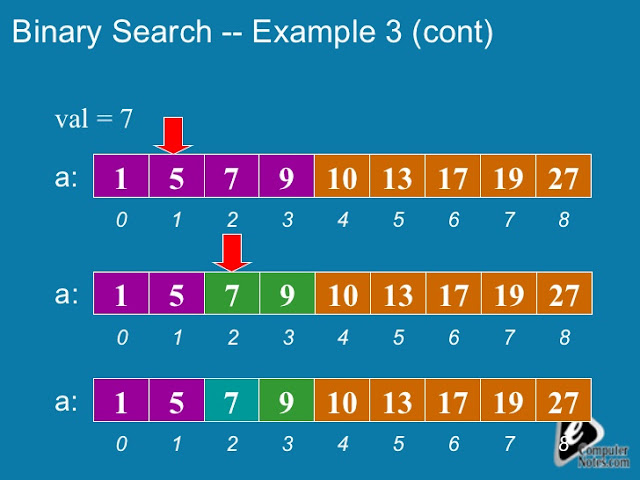
a) Implementation of Binary search mechanism
Aim: To write a JAVA program to search for an element in a given list of elements using binary search mechanism
Description:
Program:
import java.util.Scanner;
class binarysearchdemo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int n, i, num,first, last, middle;
int a[ ]=new int[20];
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter total number of elements:");
n = s.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter elements in sorted order:");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
a[i] = s.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the search value:");
num = s.nextInt();
first = 0;
last = n - 1;
middle = (first + last)/2;
while( first <= last )
{
if ( a[middle] < num )
first = middle + 1;
else if ( a[middle] == num )
{
System.out.println("number found");
break;
}
else
{
last = middle - 1;
}
middle = (first + last)/2;
}
if ( first > last )
System.out.println( " Number is not found");
}
}
II B.Tech II Sem CSE Java Lab Exercise - 1 d(Basics)
d) A case study
Aim: A case study on public static void main(250 words)
Case study:

The program structure of a simple java program is given below with different steps
Step-1:
Click start+run and then type notepad in run dialog box and click OK. It displays Notepad.
Step-2:
In run dialogbox type cmd and click OK. It displays command prompt.
Step-3:
Type the following program in the Notepad and save the program as “example.java” in a current working directory.
class example
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println(“Welcome”);
}
}
Step-4 (Compilation): To compile the program type the following in current working directory and
then click enter.
c:\xxxx >javac example.java
Step-5 (Execution): To run the program type the following in current working directory and then
click enter.
c:\xxxx>java example
Explanation:
Generally the file name and class name should be same. If it is not same then the java file can be compiled but it cannot be executed. That is when execution it gives the following error
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: ex
In “public static void main(String args[])” statement
public is an access specifier. If a class is visible to all classes then public is used
main() must be declared as public since it must be called by outside of its class.
The keyword static allows main() to be called without creating object of the class.
The keyword void represents that main( ) does not return a value.
The main method contains one parameter String args[].
We can send some input values (arguments) at run time to the String args[] of the main
method . These arguments are called command line arguments. These command line
arguments are passed at the command prompt.
In System.out.println("Welcome"); statement
System is a predefined class that provides access to the system.
out is the output stream.
println() method display the output in different lines. If we use print() method it display the
output in the same line
II B.Tech II Sem CSE Java Lab Exercise - 1 c(Basics)
c) Bike Race
Aim: Five Bikers Compete in a race such that they drive at a constant speed which may or may not be the same as the other. To qualify the race, the speed of a racer must be more than the average speed of all 5 racers. Take as input the speed of each racer and print back the speed of qualifying racers.
Description:
Program:
import java.util.*;
class racedemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
float s1,s2,s3,s4,s5,average;
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter speed of first racer:");
s1 = s.nextFloat();
System.out.println("Enter speed of second racer:");
s2 = s.nextFloat();
System.out.println("Enter speed of third racer:");
s3 = s.nextFloat();
System.out.println("Enter speed of fourth racer:");
s4 = s.nextFloat();
System.out.println("Enter speed of fifth racer:");
s5 = s.nextFloat();
average=(s1+s2+s3+s4+s5)/5;
if(s1>average)
System.out.println("First racer is qualify racer:");
else if(s2>average)
System.out.println("Second racer is qualify racer:");
else if(s3>average)
System.out.println("Third racer is qualify racer:");
else if(s4>average)
System.out.println("Fourth racer is qualify racer:");
else if(s5>average)
System.out.println("Fifth racer is qualify racer:");
}
}
II B.Tech II Sem CSE Java Lab Exercise - 1 b(Basics)
b) Roots of a quadratic equation
Aim: To write a java program that display the roots of a quadratic equation ax2+bx=0. Calculate the discriminate D and basing on value of D, describe the nature of root.
Description:
import java.util.*;
class quadraticdemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a, b, c;
double r1, r2, D;
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Given quadratic equation:ax^2 + bx + c");
System.out.print("Enter a:");
a = s.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter b:");
b = s.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter c:");
c = s.nextInt();
D = b * b - 4 * a * c;
if(D > 0)
{
System.out.println("Roots are real and unequal");
r1 = ( - b + Math.sqrt(D))/(2*a);
r2 = (-b - Math.sqrt(D))/(2*a);
System.out.println("First root is:"+r1);
System.out.println("Second root is:"+r2);
}
else if(D == 0)
{
System.out.println("Roots are real and equal");
r1 = (-b+Math.sqrt(D))/(2*a);
System.out.println("Root:"+r1);
}
else
{
System.out.println("Roots are imaginary");
}
}
}
Output:
II B.Tech II Sem CSE Java Lab Exercise - 1a (Basics)
a) Displaying default value of all primitive data types
Aim: To write a JAVA program to display default value of all primitive data type of JAVA
Description:
Program:
class defaultdemo
{
static byte b;
static short s;
static int I;
static long l;
static float f;
static double d;
static char c;
static boolean bl;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("The default values of primitive data types are:");
System.out.println("Byte :"+b);
System.out.println("Short :"+s);
System.out.println("Int :"+i);
System.out.println("Long :"+l);
System.out.println("Float :"+f);
System.out.println("Double :"+d);
System.out.println("Char :"+c);
System.out.println("Boolean :"+bl);
IT JNTUK R19 SYLLABUS (1-1 and 1-2)
DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY COURSE STRUCTURE AND SYLLABUS
For
B. Tech INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
(Applicable for batches admitted from 2019-2020)
IT JNTUK R16 SYLLABUS
R16 COURSE STRUCTURE AND SYLLABUS
Web Technologies UNIT-3 R16
UNIT-3
XML
AND
AJAX A New Approach
Web Technologies UNIT-2 R16
UNIT-2
Javascript
AND
DHTML
Web Technologies UNIT-1 R16
Principle of Programming Language UNIT-3
UNIT-3
Subprograms and implementations
Principle of Programming Language UNIT-2
UNIT-2
Data, data types, and basic statements
Principle of Programming Language UNIT-1
UNIT-1------------Syntax and semantics