- Configuring RAID
RAID Mirroring means an exact clone (or mirror) of the same data writing to two drives. A minimum two number of disks are more required in an array to create RAID1 and it’s useful only, when read performance or reliability is more precise than the data storage capacity.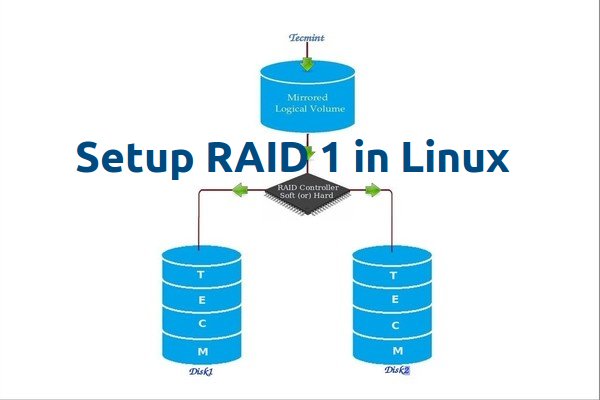

Mirrors are created to protect against data loss due to disk failure. Each disk in a mirror involves an exact copy of the data. When one disk fails, the same data can be retrieved from other functioning disk. However, the failed drive can be replaced from the running computer without any user interruption.
Features of RAID 1
- Mirror has Good Performance.
- 50% of space will be lost. Means if we have two disk with 500GB size total, it will be 1TB but in Mirroring it will only show us 500GB.
- No data loss in Mirroring if one disk fails, because we have the same content in both disks.
- Reading will be good than writing data to drive.
Requirements
Minimum Two number of disks are allowed to create RAID 1, but you can add more disks by using twice as 2, 4, 6, 8. To add more disks, your system must have a RAID physical adapter (hardware card).
Here we’re using software raid not a Hardware raid, if your system has an inbuilt physical hardware raid card you can access it from it’s utility UI or using Ctrl+I key.
My Server Setup
This article will guide you through a step-by-step instructions on how to setup a software RAID 1 or Mirror using mdadm(creates and manages raid) on Linux Platform. Although the same instructions also works on other Linux distributions such as RedHat, CentOS, Fedora, etc.
Step 1: Installing Prerequisites and Examine Drives
1. As I said above, we’re using mdadm utility for creating and managing RAID in Linux. So, let’s install the mdadm software package on Linux using yum or apt-get package manager tool.
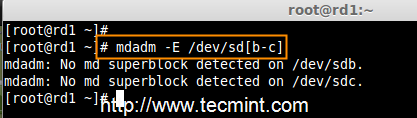
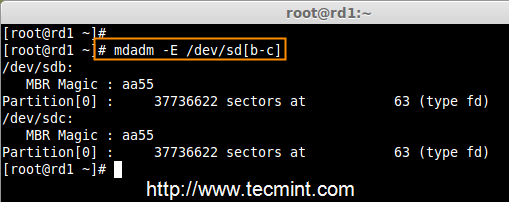
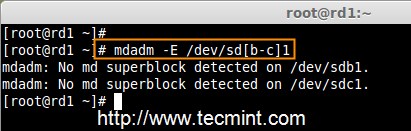
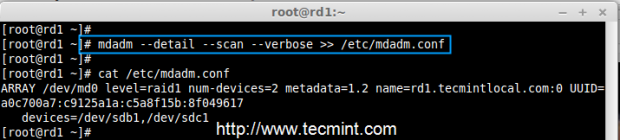
2. Once ‘mdadm‘ package has been installed, we need to examine our disk drives whether there is already any raid configured using the following command.
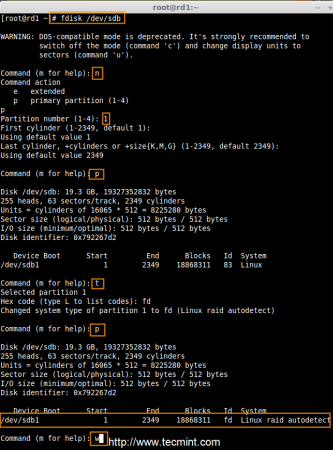
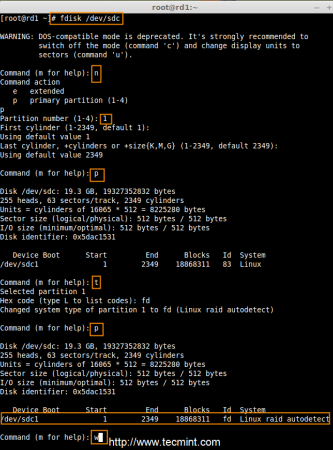
Step 2: Drive Partitioning for RAID
Follow the below instructions
- Press ‘n‘ for creating new partition.
- Then choose ‘P‘ for Primary partition.
- Next select the partition number as 1.
- Give the default full size by just pressing two times Enter key.
- Next press ‘p‘ to print the defined partition.
- Press ‘L‘ to list all available types.
- Type ‘t‘to choose the partitions.
- Choose ‘fd‘ for Linux raid auto and press Enter to apply.
- Then again use ‘p‘ to print the changes what we have made.
- Use ‘w‘ to write the changes.
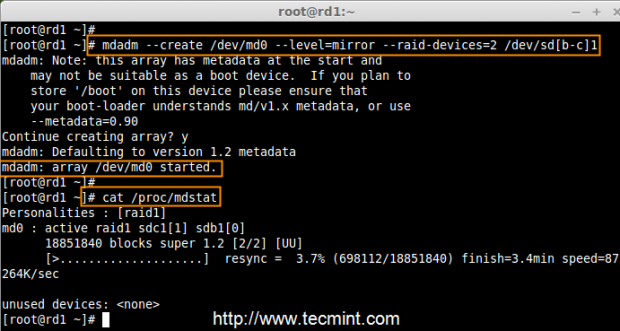
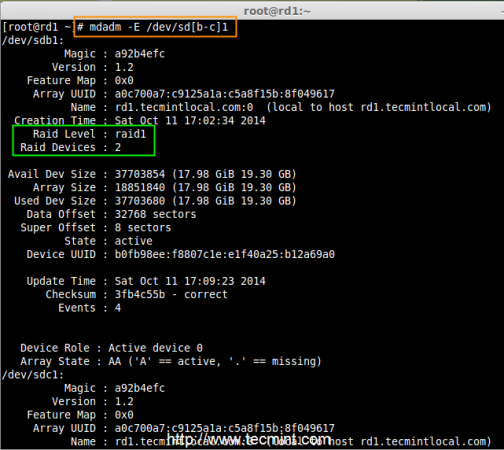
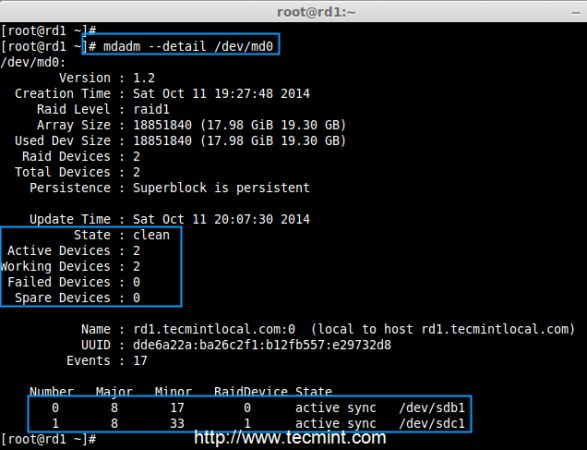
Step 3: Creating RAID1 Devices
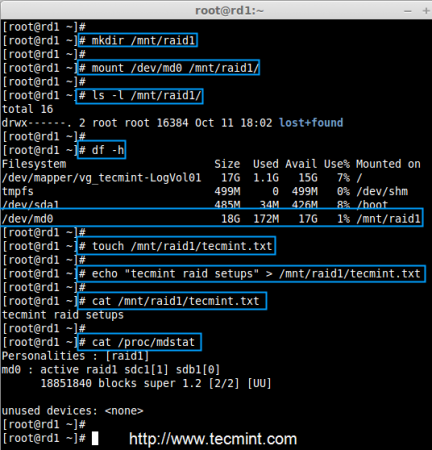
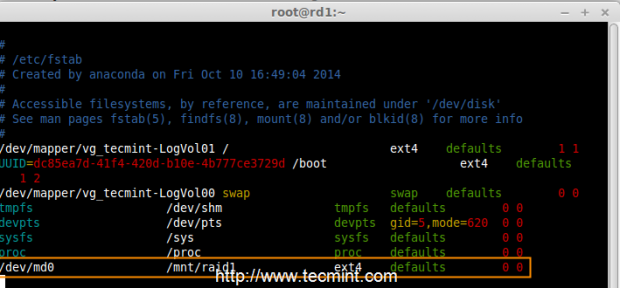
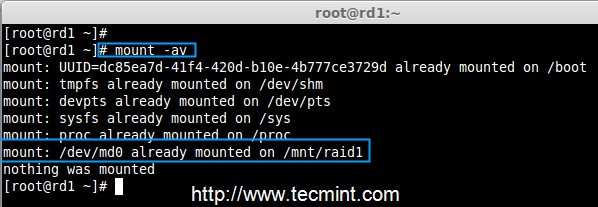
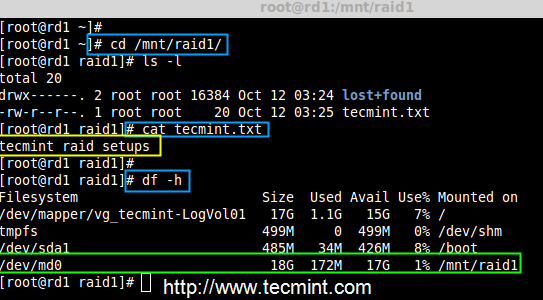
Step 4: Creating File System on RAID Device
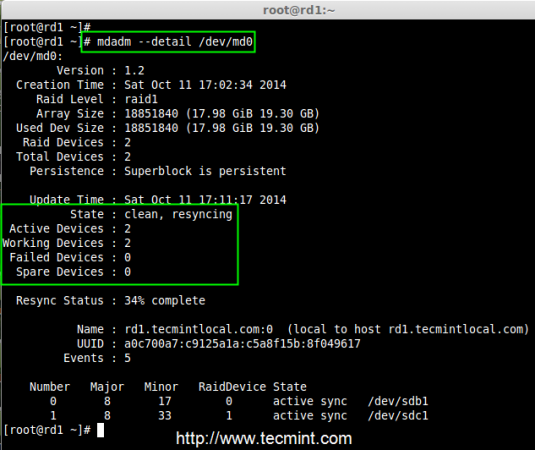
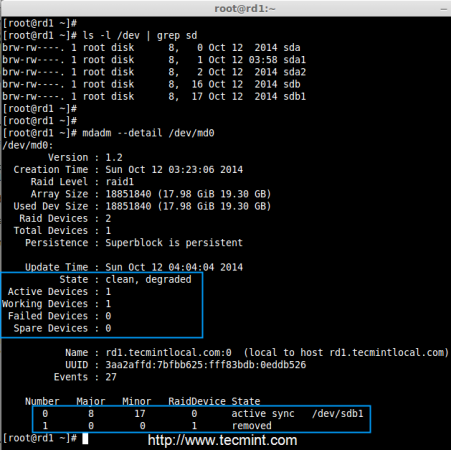
Step 5: Verify Data After Disk Failure
yum install mdadm [on RedHat systems]
# apt-get install mdadm [on Debain systems]

No comments